In week 4, we learned detail about prokaryotic cell. After learning this topic, we able to list down and identify the important structures of prokaryotic cells and able to explain the characteristics of functions of the structures of prokaryotic cell. Then, Dr wan told us about Helicobacter pyolori. H. pylori are spiral-shaped bacteria that grow in the digestive tract and have a tendency to attack the stomach lining. H. pylori infections are usually harmless, but they’re responsible for the majority of ulcers in the stomach and small intestine.
H. pylori is a common type of bacteria that usually infects the stomach. They may be present in more than half of all people in the world, according to the Mayo Clinic. The “H” in the name is short for Helicobacter. “Helico” means spiral. The bacteria are spiral shaped.
H. pylori normally infect your stomach during childhood. While infections with this strain of bacteria typically don’t cause symptoms, they can lead to diseases in some people, including peptic ulcers, and an inflammatory condition inside your stomach known as gastritis.
H. pylori are adapted to live in the harsh, acidic environment of the stomach. These bacteria can change the environment around them and reduce its acidity so they can survive. The shape of H. pylori allows them to penetrate your stomach lining, where they’re protected by mucus and your body’s immune cells are not able to reach them. The bacteria can interfere with your immune response and ensure that they’re not destroyed. This can lead to stomach problems.
 |
| Helicobacter pylori |
Then, inside the lecture notes, Dr Wan prepare some questions that we needed to find the answer so that we can ready for the lecturer. Dr Wan explained to us about gram staining. Gram staining will give result gram positive or gram negative and gram staining for bacteria only. Most gram negative are bacillus but not all while E.coli is a gram negative. Gram negative has thinner peptidoglycan, more pathogenic (lipopolysaccharide), resistant to antibiotic and have enzyme called beta-lactamase in periplasmic space. Beta-lactamase can digest beta-lactamerin. Gram positive have thicker peptidoglycan. Carboxisome is in the part of inclusions body. Endotoxin is in order toxin to release, bacteria need to suicide (they have to die). Exotoxin is more virulent because they do even die and can release toxin. Afla is toxin produce by fungi while Alfa is toxin released by bacteria. Safranin can give color in gram negative for counter stain before decolorisation. Chelating agent is binding agent.
| Prokaryotic cell |
These are the causes a species to have a particular size or shape. This is because efficient nutrient uptake and decreased susceptibility to predation. Normal concentration of salt is 1.5 M. Halophiles is a extra concentration of salt to survive. Methanogen bacteria can be found usually at volcano and under water habitat for methanogens deep-sea-vent (hydrothermal vent) volcano under the sea.
| External structure |
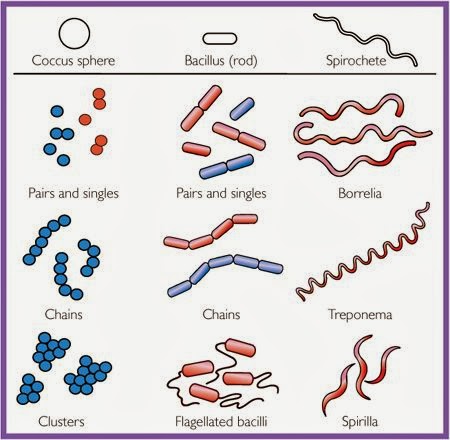 |
| Bacterial shape and arrangements |
Lichen is associations of algae and fungus, like clean environment, clean from pollutant and act as biological indicator. Bioremediation is used of microbe to remove pollutant such as mushrooms. Phytoremediation is used plant to remove pollutant. Mycology is the study of fungus and mycoremediation is used fungi as remediation.
Common bacterial and archaeal structures are plasma membrane, gas vacuole, ribosomes, inclusions, nucleoid, periplasmic space, cell wall, capsules and sliming layers, fimbrae and pili, flagella and endospore. We also play a quiz online on quizzlet about the structure of prokaryote. Structures external to the cell wall are glycocalyx, flagella, axial filaments and fimbrae and pili. Glycocalyx is the source of nutrient that made up of polysaccharide and polypeptide (sugar). Certain microbe needs vectors to move around. Termites lived in insect. Termites get nutrient from bacteria. Bacteria do not have cilia but it have fimbrae and pili.
| External structure |
| Glycocalyx surrounding the cell wall |
There are many techniques to study motility of bacteria. For example motility test medium, flagella stain and direct microscopic stain. Three types of motility are "run" or "swim", "tumbles" and "swarm". Advantages of motility is ability to move toward a favorable environment or away from an adverse one (known) as taxis. Type of stimuli are chemical and light. Chemical is for chemotaxis while light for phototaxis.
Function of cell wall are responsible for shape cell, prevent bacterial cells from rupturing due to changes in pressure, the point of anchorage for flagella and may contain antigen if bacteria is infectious. There are gram positive cell wall and gram negative cell wall. Atypical cell wall is certain types of prokaryotes that have no cell wall for example Mycoplasma. Atypical cell wall also included with special content of cell wall for example Mycobacterium. Movement of materials across membranes have two processes which are passive process and active process. Passive process is substances cross from area of high concentration to low concentration (with concentration of gradient). Active transport is movement from area of low concentration to high concentration (against concentration gradient).
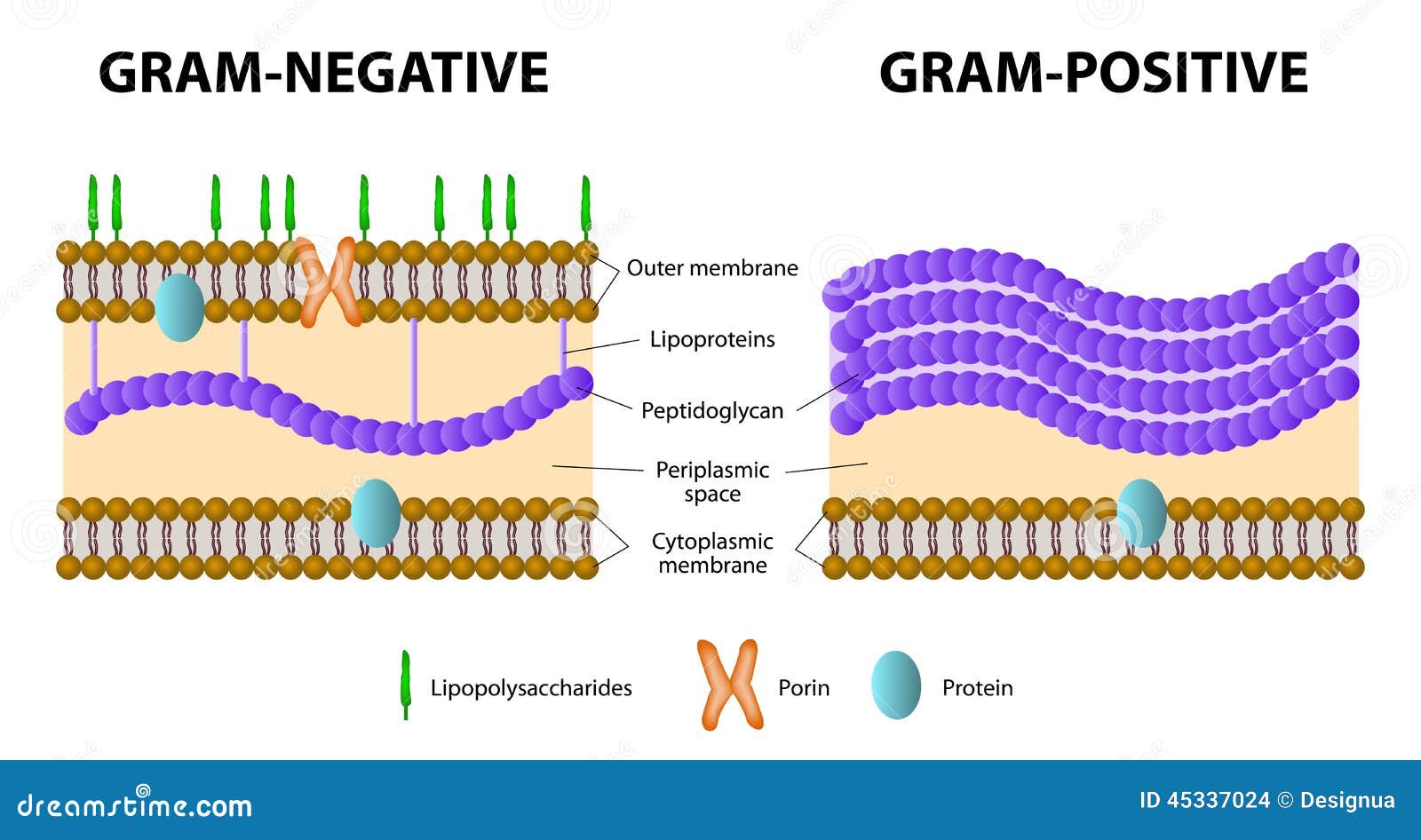 |
| Gram positive and gram negative |
Cytoplasm is substance of the cell inside the plasma membrane. 80% water and primarily contains proteins (enzymes), carbohydrates, lipids and etc. Major structures in cytoplasm are nuclear area, ribosomes and inclusions.The liquid part inside the cytoplasm called cytosol.
No comments:
Post a Comment